User Authentication Methods and Managed Users
Devices to manage with the Access Management System have the following three user authentication methods, and each method manages different types of users.
|
User Authentication Method
|
Description
|
|
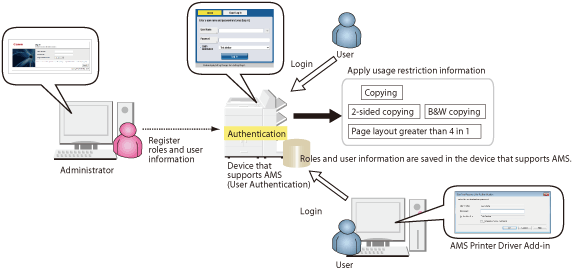
Local Device Authentication
|
Performs user information management and user authentication at the device. When a user enters a user name and password on a device, user authentication is performed based on local user information registered in the device.
|
|
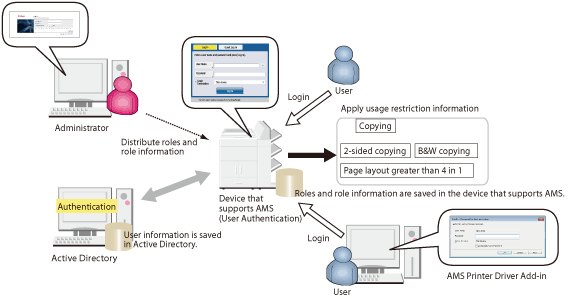
Active Directory Authentication
|
Uses domain user information registered in Active Directory to perform user authentication. When a user enters a user name and password, user authentication is performed by Active Directory.
|
|
Local Device Authentication + Active Directory Authentication, or Local Device Authentication + LDAP Authentication
|
These user authentication methods support both server authentication/local device authentication for Active Directory authentication and local device authentication or LDAP authentication and local device authentication. For example, this can enable you to manage users registered in the authentication server (such as regular employees) using Active Directory authentication/LDAP authentication, and temporary users (such as contract employees) using local device authentication.
As this user authentication method also enables you to use devices with local device authentication when you cannot access the authentication server for a reason such as network trouble, it is recommended that you operate the Access Management System using these methods.
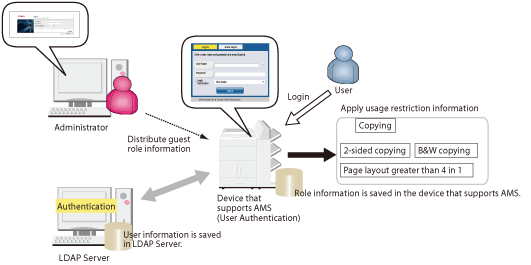
LDAP authentication uses user information registered on an LDAP server to authenticate users.
|
Local Device Authentication Method
Active Directory Authentication
LDAP Authentication
|
NOTE
|
|
When using Local Device Authentication + Active Directory Authentication, or Local Device Authentication + LDAP Authentication, the location for authentication differs according to the type of user that logs in.
|