Specifying a File Server Using the Keyboard
You can specify a file server as the destination directly from the keyboard displayed on the touch panel display. Press [Host Name], [Folder Path], [User Name], and [Password] to specify the file server settings.
1.
Press [Scan and Send] → [New Destination].
2.
Press [File].
3.
Press the drop-down list → select the desired server protocol.
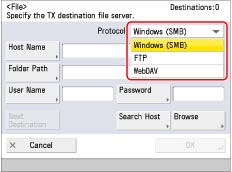
You can use the following server protocols.
Confirm the system environment of the destination before sending.
System Requirements for IPv4 Compatible Server:
|
Protocol
|
System Requirements
|
Application
|
|
FTP
|
Sun Solaris V.2.6 or later
Mac OS X or later
Red Hat Linux 7.2
|
-
|
|
Windows 2000 Server
|
Internet Information Services 5.0
|
|
|
Windows XP Professional
|
Internet Information Services 5.1
|
|
|
Windows Server 2003
|
Internet Information Services 6.0
|
|
|
Windows Vista
Windows Server 2008
|
Internet Information Services 7.0
|
|
|
Windows 7
Windows Server 2008 R2
|
Internet Information Services 7.5
|
|
|
Windows(SMB)
|
Windows 2000/XP
Windows Server 2003
Windows Vista
Windows Server 2008
Windows 7
|
-
|
|
Mac OS X v10.2
Red Hat Linux 7.2
|
Samba 2.2/3.0
|
|
|
WebDAV
|
Sun Solaris V.2.6 or later
Red Hat Enterprise Linux AS/ES/WS 4.0 or later
Windows 2000 Server
Windows XP Professional
Windows Server 2003
Windows Vista
Windows Server 2008
|
Apache 2.0
|
|
Mac OS X
|
Apache 1.3
|
|
|
Windows 7
Windows Server 2008 R2
|
Apache 2.0
|
|
|
Windows 2000 Professional
Windows 2000 Server
|
Internet Information Services 5.0
|
|
|
Windows XP Professional
|
Internet Information Services 5.1
|
|
|
Windows Server 2003
|
Internet Information Services 6.0
|
|
|
Windows Vista
Windows Server 2008
|
Internet Information Services 7.0
|
|
|
Windows 7
Windows Server 2008 R2
|
Internet Information Services 7.5
|
System Requirements for IPv6 Compatible Server:
|
Protocol
|
System Requirements
|
Application
|
|
FTP
|
Solaris Version 9.0 or later
Red Hat Enterprise Linux AS/ES/WS 4.0 or later
Mac OS X 10.3 or later
|
-
|
|
Windows 7
Windows Server 2008 R2
|
Internet Information Services 7.5
|
|
|
Windows(SMB)
|
Windows 2000/XP
Windows Server 2003
Windows Vista
Windows Server 2008
Windows 7
|
-
|
|
WebDAV
|
Solaris Version 9.0 or later
|
Apache 2.0
|
|
Windows Server 2003
|
Internet Information Services 6.0
|
|
|
Windows 7
Windows Server 2008 R2
|
Internet Information Services 7.5
|
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
If you are using WebDAV and connect to the Internet using a proxy server, the proxy server must support IPv6.
|
4.
Specify each setting.
Specifying the File Server Using [Browse]
If you select [Windows(SMB)] as the server protocol, you can specify the file server by pressing [Browse]. For instructions on setting the resolution, see "Specifying a File Server Using the Browse Key (Windows (SMB))."
Specifying the File Server Using [Search Host]
If you select [Windows(SMB)] as the server protocol, you can specify the file server by pressing [Search Host]. For instructions on using the Search Host key, see "Specifying a File Server Using the Search Host Key (Windows (SMB))."
Specifying a Destination by Entering a File Server
Press each item and enter them using the keyboard.
|
Item
|
Description
|
|
Host Name
|
A host name is a name assigned to a host computer that provides services on the Internet. A specific host name is assigned to each host computer to identify it on the Internet. In this entry box, enter the name of the file server on the network as the destination of the send job.
If you select [FTP] or [WebDAV] as the server protocol, you can also specify a port number after the host name address by entering a colon (:) and the port number.
Example: 192.168.100.50:21000
When sending to an IPv6 host, specify the following settings for [Host Name].
[IPv6 Address]: <Port Number>
Example: [5aed:90a0:bc05:01d2:568a:2fc0:0001:12ee]:21000
Make sure to enter the same port number for the Host Name as the one specified for the FTP server or WebDAV server to which you are sending your documents.
|
|
Folder Path
|
A folder path is a series of characters that signify the location of the folder. Specify a folder in the file server as the destination of the send job.
|
|
User Name
|
The login user name for the file server.
To enter the user name only:
Example: user_name
Maximum 20 characters
To enter the user name and the domain name:
Example: domain_name\user_name
Domain name: Maximum 15 characters
User name: Maximum 20 characters
To enter a UPN (User Principal Name):
Example: user_name@domain_name.com
Maximum 128 characters
|
|
Password
|
The login password for the file server.
|
To add another destination, press [Next Destination] → repeat the procedure above.
|
NOTE
|
|
If you select [WebDAV] as the server protocol, the HTTP protocol is used if you specify 'HTTP://' as the scheme at the start of the host name. The SSL + HTTP (HTTPS) protocol is used if you specify 'HTTPS://' as the scheme at the start of the host name. Specifying 'HTTPS://' as the scheme enables SSL communications between the server and the machine. However, the route between the server and the machine is only encrypted, and a server certificate validity check is not performed using a CA certificate.
You can only use UPN (User Principal Name) if you are sending to a computer belonging to a domain operated with Active Directory.
When sending to a file server on the Internet using WebDAV, proxy server settings may be required, depending on the environment of the destination. (See "Settings Common to TCP/IPv4 and TCP/IPv6.")
|
5.
Press [OK].