TCP/IPv4 Settings
This section describes the procedure for setting TCP/IPv4 using the control panel. After specifying the settings for TCP/IPv4, follow the procedure in "Settings Common to TCP/IPv4 and TCP/IPv6" to specify the required settings, and the procedure in "Confirming TCP/IPv4 Settings (PING Command)" to check whether the network settings are correct. If the settings for TCP/IPv6 are already specified and you have finished specifying the settings common to TCP/IPv4 and TCP/IPv6, only check the network settings after completing this procedure.
If you want to use IPv6 communications at the same time, follow the procedure in "TCP/IPv6 Settings" to specify the required settings, and the procedure in "Confirming TCP/IPv6 Settings (PING Command)" to confirm the settings.
1.
Press  (Settings/Registration).
(Settings/Registration).
 (Settings/Registration).
(Settings/Registration).2.
Press [Preferences] → [Network].
3.
Press [TCP/IP Settings] → [IPv4 Settings].
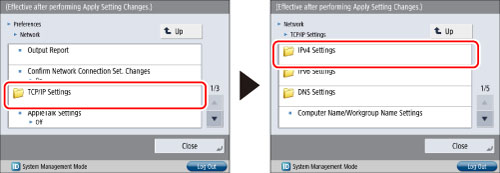
4.
Press [Use IPv4] for [IPv4 Settings] → [On] → [OK].
If you select [Off] for <Use IPv4>, IPv4 networks cannot be used, regardless of the settings specified for IPv4 on the Settings/Registration screen. The ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) table is also disabled.
5.
Press [IP Address Settings] for [IPv4 Settings] → specify the following items → press [OK].
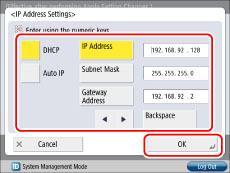
Automatically obtaining an IP address:
Select 'On' for either [DHCP] or [Auto IP].
You can also set both [DHCP] and [Auto IP] to 'On'. If both [DHCP] and [Auto IP] have been enabled, priority is given to DHCP when obtaining an IP address. If [DHCP] was unable to obtain the IP address, [Auto IP] will then automatically attempt to obtain the IP address.
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
It takes about two minutes to check whether the Auto IP or DHCP settings can be used. If you do not plan to use one of these settings, it is recommended that you turn them off.
|
|
NOTE
|
|
If the machine is restarted after DHCP or Auto IP settings are specified, the TCP/IP Settings screen displays the IP address setting values. (If the IP address, host name, and domain name have been previously set, these will be overwritten by the setting values obtained from DHCP or Auto IP settings.)
If you use DHCP without the DNS dynamic update function, it is recommended that an identical IP address be assigned to the machine at all times. (If the IP address is not identical, the host name for the machine will not correspond to the IP address.)
If the IP address was successfully obtained by Auto IP, the subnet mask will become 255.255.0.0 and the gateway address will become 0.0.0.0.
|
If you set [DHCP] to 'On' in [IP Address Settings], specify the DHCP option settings. If you set [DHCP] to 'Off', proceed to step 7.
Manually obtaining an IP address:
Select 'Off' for either [DHCP] or [Auto IP].
Press [IP Address] → enter the IP address.
Press [Subnet Mask] → enter the subnet mask.
Press [Gateway Address] → enter the gateway address.
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
If the IP address could not be obtained by DHCP or Auto IP, enter [IP Address], [Subnet Mask], and [Gateway Address].
|
6.
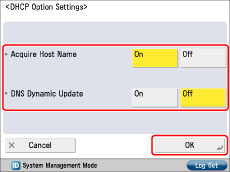
Press [DHCP Option Settings] for [IPv4 Settings] → specify the following settings → press [OK].
|
[Acquire Host Name]
|
You can automatically obtain the host name from the DHCP server.
|
|
[DNS Dynamic Update]
|
You can automatically register the IPv4 address, host name, domain name set for the machine in the DNS server using dynamic DNS updating. A dynamic DNS server is required for using dynamic DNS updating.
|
7.
Press [Up].
8.
Press [DNS Settings] for [TCP/IP Settings].
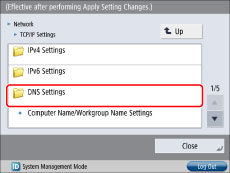
If you are using Windows, or if you are not using Bonjour on the Macintosh, proceed to step 10.
9.
Press [mDNS Settings] for [DNS Settings] → specify the following items → press [OK].
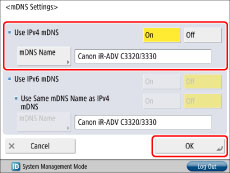
To use the DNS function on a system that does not have a DNS server, press [On] for <Use IPv4 mDNS>.
To change the mDNS name, press [mDNS Name] → enter the new mDNS name → press [OK].
If this setting has already been performed, proceed to step 13.
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
If you set <Use IPv4 mDNS> to 'On', the machine will not enter a complete Sleep mode.
|
|
NOTE
|
|
"Canon <product name>" is automatically set, if you do not change the mDNS name. If the same mDNS name already exists on the network, the name will become "Canon <product name>****** ("******" represents the last six digits of a MAC address.)"
e.g.) Canon iR-ADV C3320/3330 (7e:ec:75)
|
10.
Press [DNS Server Address Settings] for [DNS Settings] → Specify the following settings in <IPv4> → press [OK].
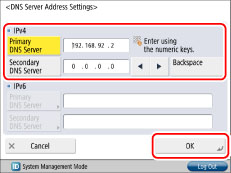
If you want to use dynamic DNS updating, enter the IPv4 address of the DNS server in [Primary DNS Server].
If you do not want to set up a secondary DNS server, enter <0.0.0.0>.
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
If you set [DHCP] to 'On' in step 5, and the DNS server IP address obtained from the DHCP server is different from the IP address set manually, the set IP address is overwritten.
If you enabled <Use IPv4 mDNS>in step 9, make sure that there are no devices on the network whose host name and mDNS name in the DNS Host/Domain Name Settings are the same. Any non-unique values set manually are automatically changed so that they are unique.
|
11.
Press [DNS Host/Domain Name Settings] for [DNS Settings] → specify the following items in <IPv4> → press [OK].
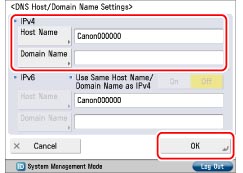
If you want to use dynamic DNS updating, it is necessary to set a host name and domain name.
Host Name: Press [Host Name] → enter the name of the machine → press [OK].
Domain Name: Press [Domain Name] → enter the name of the network domain the machine belongs to → press [OK].
Domain Name: Press [Domain Name] → enter the name of the network domain the machine belongs to → press [OK].
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
If you set [DHCP] to 'On' in step 5, the host name and domain name you set manually will be overwritten.
|
12.
Press [DNS Dynamic Update Settings] for [DNS Settings] → specify the following items in <IPv4> → press [OK].
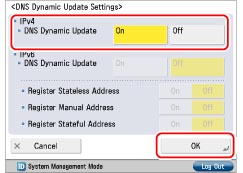
If you press [On] for <DNS Dynamic Update>, you can automatically register the IPv4 address, host name, and domain name set for the machine in the DNS server using dynamic DNS updating. A dynamic DNS server is required for using dynamic DNS updating.
|
NOTE
|
|
If you have a DHCP server running Windows Server 2003 that uses the DHCP service and want to register the machine's DNS record, configure the following settings in the DHCP server:
In the DHCP server, right-click the [Scope] icon → click [Properties]. In the [DNS] sheet of the displayed dialog box, select [Enable DNS dynamic updates according to the settings below] → [Dynamically update DNS A and PTR records only if requested by the DHCP clients].
In the Active Directory environment, right-click the icon of the DHCP server you are using → select [Properties]. In the [Advanced] sheet of the displayed dialog box, click [Credentials]. In the [DNS dynamic update credentials] dialog box, enter the user name, domain, and password for the Active Directory.
If you have a DHCPv4 server running Windows Server 2008 that uses the DHCPv4 service and want to register the machine's DNS record, configure the following settings in the DHCPv4 server:
In the DHCPv4 server, right-click the [Scope] icon → click [Properties]. In the [DNS] sheet of the displayed dialog box, select [Enable DNS dynamic updates according to the settings below] → [Dynamically update DNS A and PTR records only if requested by the DHCP clients].
In the Active Directory environment, right-click the icon of the DHCPv4 server you are using → select [Properties]. In the [Advanced] sheet of the displayed dialog box, click [Credentials]. In the [DNS dynamic update credentials] dialog box, enter the user name, domain, and password for the Active Directory.
|
13.
Press [Up] → [Up].
14.
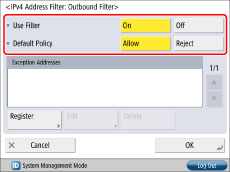
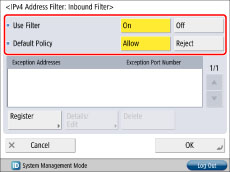
Press [Firewall Settings] for [Network] → [IPv4 Address Filter].

15.
Press [Outbound Filter] or [Inbound Filter] → specify the following settings.
 |
 |
|
[Outbound Filter]
|
[Inbound Filter]
|
By specifying the settings described below, you can filter received packets and transmitted packets using IPv4 addresses and improve security when sending and receiving data between your computer and the machine. The possibility of a third person gaining unauthorized access can be reduced by configuring the settings for [IPv4 Address Filter] in accordance with the environment you are using.
When filtering received packets and transmitted packets, you can set to allow or reject data transmission/reception between your computer and the machine. You can specify with whom you allow data transmission/reception by registering IPv4 address of a computer as an exception address.
In case of [Inbound Filter], you can register exception port number as well as the IPv4 address so that you can set which computers are allowed to use specific functions and which are rejected. For example, you can allow general users to print via print server and reject them to access to the Remote UI while administrators are allowed to use all functions.
Details of settings are shown below:
|
<Use Filter>
|
<Default Policy>
|
Settings Required after Pressing [Register]
|
|
|
Allow data transmission with all computers, but not with specified computers.
|
[On]
|
[Allow]
|
Register IPv4 address or IPv4 address prefix you want to reject.
|
|
Reject data transmission with all computers, but not with specified computers.
|
[On]
|
[Reject]
|
Register IPv4 address or IPv4 address prefix you want to allow.
|
|
Allow data reception from all computers, but not from specified computers.
|
[On]
|
[Allow]
|
Register IPv4 address or IPv4 address prefix you want to reject.
Register port number for functions you want to reject.
|
|
Reject data reception from all computers, but not from specified computers.
|
[On]
|
[Reject]
|
Register IPv4 address or IPv4 address prefix you want to allow.
Register port number for functions you want to allow.
|
|
Allow data transmission/reception with all computers.
|
[Off]
|
-
|
-
|
|
NOTE
|
|
If data transmission/reception is attempted between the device, which has the IPv4 address/port number set to be rejected, and the machine, a block log will be generated. To display the block log, "Checking the Block Log."
Information for the rejected port number is recorded in the block log only when using TCP/UDP. Port number is not recorded when using protocols which have no port number such as ICMP.
|
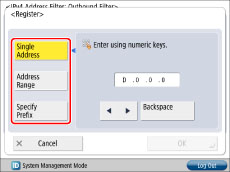
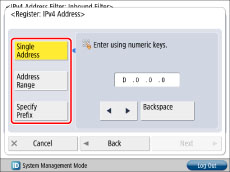
If you want to allow/reject data transmission/reception with all computers but not with specified computers
Press [Register] → set the exception IPv4 address or IPv4 address prefix.
 |
 |
|
[Outbound Filter]
|
[Inbound Filter]
|
To specify a single IPv4 address: Press [Single Address] → enter an IPv4 address.
To specify a range of IPv4 addresses: Press [Address Range] → press [First Address] → enter the first IPv4 address → press [Last Address] → specify the last IPv4 address.
To set the IPv4 address prefix: Press [Specify Prefix] → press [Address] → enter the IPv4 address prefix → press [Prefix Length] → enter the prefix length.
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
You can register up to 16 IPv4 addresses, IPv4 address ranges, or IPv4 address prefixes.
The value of [First Address] should be less than or equal to that of [Last Address].
If the usage of a protocol or print application is not permitted on your device, it cannot be used even after settings in [Firewall Settings] have been changed on your device. Configure the settings to permit the protocol or print application.
If you enter '255' in [Prefix Length], no IPv4 addresses will be set.
If you enter '0' in [Prefix Length], all IPv4 addresses will be set.
|
Press [OK] or [Next].
For [Outbound Filter], press [OK] → [OK] → proceed to step 17.
For [Inbound Filter], press [Next] → proceed to step 16.
If you want to allow/reject data transmission/reception with all computers
Confirm that [Off] is set for <Use Filter> → press [OK] → proceed to step 17.
16.
Set exception port number → press [OK] → [OK].
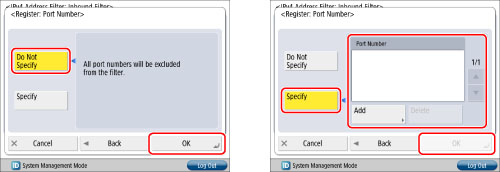
To specify all port numbers as exception: Press [Do Not Specify].
To specify port number individually: Press [Specify] → press [Add] and enter port number → press [OK].
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
You can register up to 16 port numbers for IPv4 addresses, IPv4 ranges, or IPv4 address prefixes.
You can register 50 port numbers for one port number setting.
|
17.
Press [Close].