
Managing the Logs
You can use the logs to check or analyze how the machine is being used. A variety of information about each operation is recorded in the logs, such as the operation date/time, user name, operation type, function type, and operation result. For more information on the types of logs, see System Specifications. Administrator privileges are required in order to manage the logs.
 |
If Audit Log Collection is enabled and an error occurs in the storage device managed by this function, initialization is automatically performed and then an error screen appears. If you can obtain the audit log from before the error occurred, click [Download Audit Log] to obtain the log, and then click [OK]. If you cannot obtain the audit log from before the error occurred, click [OK]. When initialization is completed, Audit Log Collection is resumed, and the automatic initialization process is recorded in the log. |
 |
You can enable <Do Not Store Personal Information in Job Log> to prevent the machine from writing personal information to the audit log. <Display Job Log> |
Starting Log Recording
Follow the procedure below to start recording logs.
Start the Remote UI  [Settings/Registration]
[Settings/Registration]  [Device Management]
[Device Management]  [Export/Clear Audit Log]
[Export/Clear Audit Log]  [Audit Log Information]
[Audit Log Information]  Click [Start] for [Audit Log Collection]
Click [Start] for [Audit Log Collection]
 [Settings/Registration]
[Settings/Registration]  [Device Management]
[Device Management]  [Export/Clear Audit Log]
[Export/Clear Audit Log]  [Audit Log Information]
[Audit Log Information]  Click [Start] for [Audit Log Collection]
Click [Start] for [Audit Log Collection] |
If Sleep Mode Energy Use is set to [Low], logs are not collected when the machine enters the Sleep mode. When generating a network connection log, mail box authentication log, mail box document operation log, or machine management log, click [Device Management]  [Save Audit Log] [Save Audit Log]  select the check box for [Save Audit Log] select the check box for [Save Audit Log]  click [OK] click [OK]  [Apply Setting Changes]. [Apply Setting Changes].When generating an Advanced Space operation log, click [Function Settings]  [Store/Access Files] [Store/Access Files]  [Advanced Space Settings] [Advanced Space Settings]  [Set Details] [Set Details]  select the check box for [Save Operation Log] select the check box for [Save Operation Log]  click [OK] click [OK]  [Apply Setting Changes]. [Apply Setting Changes].If the power of the machine is turned OFF while collecting logs due to a power outage, etc., collection starts again when the machine restarts, from the log that was being collected before the power turned OFF. If you stop log collection while logs are being collected, the logs for the period that log collection was stopped are not collected when log collection is next started. |
Exporting Logs Automatically
You can set the machine to automatically export audit logs to a specified folder at a predetermined time each day, or when the number of audit logs reaches 95% of the maximum number (approximately 38,000).
1
Start the Remote UI. Starting the Remote UI
2
Click [Settings/Registration] on the portal page. Remote UI Screen
3
Click [Device Management]  [Export/Clear Audit Log]
[Export/Clear Audit Log]  [Settings for Auto Export Audit Logs].
[Settings for Auto Export Audit Logs].
 [Export/Clear Audit Log]
[Export/Clear Audit Log]  [Settings for Auto Export Audit Logs].
[Settings for Auto Export Audit Logs].4
Select the check box for [Use Auto Export] and specify the required settings.
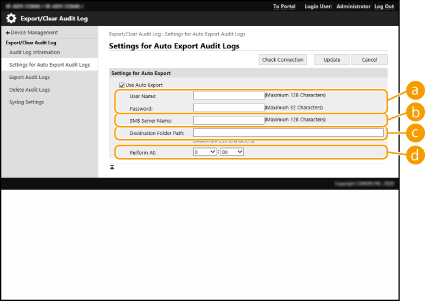
 [User Name:] / [Password:]
[User Name:] / [Password:]Enter the user name and password necessary for logging into a server to which logs are exported.
 [SMB Server Name:]
[SMB Server Name:]Enter the host name of the SMB server to export log files to, along with the path that requires authentication.
\\Host Name
\\IP Address\Shared Folder Name
 [Destination Folder Path:]
[Destination Folder Path:]Enter the path for the folder in which to store the log files.
 [Perform At:]
[Perform At:]You can specify the time at which to perform exporting.
5
Click [Check Connection], confirm that you can connect, and then click [Update].
Audit logs will now be automatically exported. The file extension is "csv."
 |
After automatic exporting of the audit logs has succeeded, the collected audit logs are automatically deleted. Audit logs cannot be deleted manually. After automatic exporting and deleting of the audit logs have succeeded, each log is generated. If other log collections do not occur by the next automatic export time, the audit log will not be automatically exported. You can also manually export audit logs from the Remote UI. Exporting a Log as a File If automatic exporting fails, the machine will retry multiple times. An error message is displayed on the control panel of the machine if automatic exporting fails even once. Specify an SMB server for Windows Server 2016 or later, or Windows 10 or later. If the machine is turned OFF, exporting will not be performed, even at the specified time. Also, it will not be performed when the machine recovers. If the machine is in the Sleep mode, it will automatically recover and perform exporting at the specified time. Note that if you are using a server that does not support SMB 3.0/3.1 encrypted communication, audit log data travels unencrypted across communication paths while it is being automatically exported. Depending on your environment, automatic exporting of logs may be performed later than the specified time. |
6
Follow the instructions on the screen to specify the location to store the files.
The csv files are stored.
Exporting a Log as a File
The various logs can be exported and saved to a computer as CSV files, which can be opened using a CSV file editor or a text editor.
 |
When exporting logs as files, use TLS or IPSec. Configuring the IPSec Settings |
Start the Remote UI  [Settings/Registration]
[Settings/Registration]  [Device Management]
[Device Management]  [Export/Clear Audit Log]
[Export/Clear Audit Log]  [Export Audit Logs]
[Export Audit Logs]  [Export]
[Export]  Follow the on-screen instructions to save the file
Follow the on-screen instructions to save the file
 [Settings/Registration]
[Settings/Registration]  [Device Management]
[Device Management]  [Export/Clear Audit Log]
[Export/Clear Audit Log]  [Export Audit Logs]
[Export Audit Logs]  [Export]
[Export]  Follow the on-screen instructions to save the file
Follow the on-screen instructions to save the fileIf you want to automatically delete all logs after they are exported, select the check box for [Delete logs from device after export] before clicking [Export]. If you then click [Cancel], exporting is canceled and the logs are deleted, even if they were not finished being exported as files.
Log collection is stopped while the export process is being performed.
Deleting the Logs
You can delete all of the collected logs.
Start the Remote UI  [Settings/Registration]
[Settings/Registration]  [Device Management]
[Device Management]  [Export/Clear Audit Log]
[Export/Clear Audit Log]  [Delete Audit Logs]
[Delete Audit Logs]  [Delete]
[Delete]  [Yes]
[Yes]
 [Settings/Registration]
[Settings/Registration]  [Device Management]
[Device Management]  [Export/Clear Audit Log]
[Export/Clear Audit Log]  [Delete Audit Logs]
[Delete Audit Logs]  [Delete]
[Delete]  [Yes]
[Yes] |
If [Settings for Auto Export Audit Logs] is enabled, you cannot manually delete audit logs. |
Sending Logs via the Syslog Protocol
Syslog Information can be sent to an SIEM (security information/event management) system. Linking with an SIEM system enables various information analyzed from realtime alert information to be centrally managed.
1
Start the Remote UI. Starting the Remote UI
2
Click [Settings/Registration] on the portal page. Remote UI Screen
3
Click [Device Management]  [Export/Clear Audit Log]
[Export/Clear Audit Log]  [Syslog Settings].
[Syslog Settings].
 [Export/Clear Audit Log]
[Export/Clear Audit Log]  [Syslog Settings].
[Syslog Settings].4
Select [Use Syslog Send], and specify the required settings.
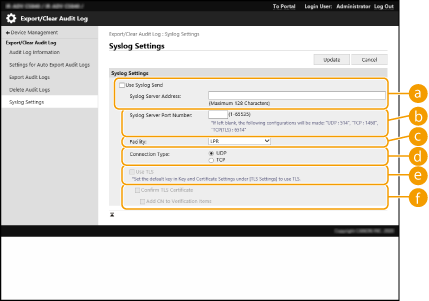
 [Syslog Server Address:]
[Syslog Server Address:]Specify the address of the Syslog server to connect to. Enter the necessary information, such as IP address and host name, according to your environment.
 [Syslog Server Port Number:]
[Syslog Server Port Number:]Enter the port number used by the Syslog server for Syslog communication. If left blank, the port number defined in RFC (UDP: 514, TCP: 1468, TCP (TLS): 6514) is used.
 [Facility:]
[Facility:]Specify the type of log messages to send. Select one of the following: [Local0] to [Local7], [Log Alert], [Log Audit], [Security Messages], or [LPR] defined in RFC.
 [Connection Type:]
[Connection Type:]Specify the communication type ([UDP]/[TCP]).
 [Use TLS]
[Use TLS]Select this to use TLS to encrypt information communicated with the Syslog server.

When [TCP] is selected in [Connection Type:], you can set to use TLS.
 [Confirm TLS Certificate]/[Add CN to Verification Items]
[Confirm TLS Certificate]/[Add CN to Verification Items]Set whether to verify the TLS server certificate sent when connecting and its CN (Common Name).
5
Click [Update].
 |
A slight time lag occurs after the error for some audit logs, because Syslog transmission is performed after polling every 30 seconds. The supported RFCs are 5424 (Syslog format), 5425 (TLS), and 5426 (UDP). |