Spezifikationen der Sicherheits- und Verwaltungsfunktionen
Firewall
Es können bis zu 16 IP-Adressen (oder Bereiche von IP-Adressen) sowohl für IPv4 als auch für IPv6 angegeben werden.
Es können bis zu 32 MAC-Adressen angegeben werden.
Schlüssel und Zertifikate
Die folgenden Schlüssel und Zertifikate werden unterstützt:
Selbstgenerierter Schlüssel und selbstsigniertes Zertifikat oder CSR
Algorithmus des öffentlichen Schlüssels (und Schlüssellänge) | RSA (512 Bits, 1024 Bits, 2048 Bits, 4096 Bits) DSA (1024 Bits, 2048 Bits, 3072 Bits) ECDSA (P256, P384, P521) |
Algorithmus zur Signatur von Zertifikaten | RSA: SHA-1*1, SHA-256, SHA-384*2, SHA-512*2 DSA: SHA-1*1 ECDSA: SHA-1*1, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512 |
*1 Nur verfügbar, wenn die Installation über Remote UI erfolgt.
*2 SHA384-RSA und SHA512-RSA sind nur verfügbar, wenn die RSA-Schlüssellänge 1024 Bits oder mehr beträgt.
Schlüssel und Zertifikat oder ZS-Zertifikat für die Installation
Format | Schlüssel PKCS#12*1*2 ZS-Zertifikat X.509 DER-Format/PEM-Format*2 |
Dateierweiterung | Schlüssel ".p12" oder ".pfx" ZS-Zertifikat ".cer" oder ".pem" |
Algorithmus des öffentlichen Schlüssels (und Schlüssellänge) | RSA (512 Bits, 1024 Bits, 2048 Bits, 4096 Bits) DSA (1024 Bits, 2048 Bits, 3072 Bits) ECDSA (P256, P384, P521) |
Algorithmus zur Signatur von Zertifikaten | RSA: SHA-1*3, SHA-256, SHA-384*4, SHA-512*4 DSA: SHA-1*3 ECDSA: SHA-1*3, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512 |
*1 Die Anforderungen für das in einem Schlüssel enthaltene Zertifikat entsprechen denen für ZS-Zertifikate.
*2 Zertifikate mit mehr als 2 MB können nicht registriert werden.
*3 Nur verfügbar, wenn die Installation über Remote UI erfolgt.
*4 SHA384-RSA und SHA512-RSA sind nur verfügbar, wenn die RSA-Schlüssellänge 1024 Bits oder mehr beträgt.
 |
Das Gerät unterstützt nicht die Verwendung einer Zertifikatssperrliste (CRL). |
Definition von "Schwache Verschlüsselung"
Wenn [Verw. v. schwacher Verschlüs. verbieten] in [Einst. Verschlüssel.] auf [Ein] gesetzt ist, ist die Verwendung der folgenden Algorithmen verboten. [Einstellungen Verschlüsselung]
Hash | MD4, MD5, SHA-1 |
HMAC | HMAC-MD5 |
Verschlüsselung mit einem gemeinsamen Schlüssel | RC2, RC4, DES |
Verschlüsselung mit öffentlichem Schlüssel | RSA-Verschlüsselung (512 Bits/1024 Bits) RSA-Signatur (512 Bits/1024 Bits) DSA-Verschlüsselung (512 Bits/1024 Bits) DH (512 Bits/1024 Bits) |
 |
Auch wenn [Schl./Zert. m. schwa. Verschlüs. verb.] in [Einst. Verschlüssel.] auf [Ein] gesetzt ist, kann der Hashalgorithmus SHA-1, der zur Signatur eines Stammzertifikats dient, verwendet werden. |
TLS
Die folgenden Kombinationen von TLS-Version und Algorithmus sind möglich:
 : Geeignet
: Geeignet  : Nicht geeignet
: Nicht geeignetAlgorithmus | TLS-Version | |||
TLS 1.3 | TLS 1.2 | TLS 1.1 | TLS 1.0 | |
Verschlüsselungsalgorithmus | ||||
AES-CBC (256 Bit) | 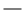 |  |  |  |
AES-CBC (128 Bit) | 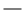 |  |  |  |
AES-GCM (256 Bit) |  |  | 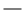 | 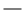 |
AES-GCM (128 Bit) |  |  | 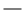 | 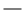 |
3DES-CBC | 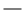 |  |  |  |
CHACHA20-POLY1305 |  | 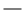 | 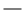 | 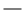 |
Schlüsselaustauschalgorithmus | ||||
RSA | 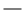 |  |  |  |
ECDHE |  |  |  |  |
X25519 |  | 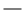 | 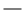 | 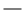 |
Signaturalgorithmus | ||||
RSA |  |  |  |  |
ECDSA |  |  |  |  |
HMAC-Algorithmus | ||||
SHA1 | 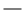 |  |  |  |
SHA256 |  |  | 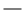 | 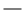 |
SHA384 |  |  | 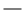 | 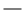 |