FTP Server Settings
Windows Server 2003/Server 2008/Vista/7/Server 2008 R2/8/Server 2012
This section describes the procedures for setting an FTP server via the control panel. Before specifying the settings on the control panel, set the FTP site via the server according to the manual provided with the OS.
It is recommended that you consult the administrator for the network you are using when configuring the FTP server.
The procedure below uses items of Windows 8 as an example. Depending on your environment, the items you see on the screen may differ.
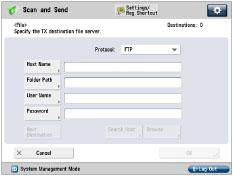
1.
Set a recipient address using the control panel.
Sample recipient settings:
Server side settings:
[Full computer name]: | example.organization.company.com |
Create a directory named "share" in the home directory, "\lnetpub\ftproot", under [Default FTP Site]/[FTP Sites], and then set "share" as the data destination.
The machine's address settings:
<Protocol:>: | FTP |
[Host Name]: | example.organization.company.com |
[Folder Path]: | share |
[User Name]: | User name entered on the server |
[Password]: | Password for the above user |
IMPORTANT |
To use the full computer name, as the host name for [Host Name] as shown in the above example, it is necessary to use a DNS server. (This applies even if the machine and the FTP server are in the same subnet.) If no DNS server is available, the setting for [Host Name] should be specified using the IP address of the FTP server. Up to 128 alphanumeric characters can be entered for [Host Name] on the control panel. Also, up to 255 alphanumeric characters can be entered for [Folder Path]. Specify the server settings within the character limits. If you change the language of the touch panel display, [Host Name] and [Folder Path] may not appear correctly. If you want to send to an IPv4 host using an FTP port other than port 21, set [Host Name] using the following format: <IPv4 address of FTP server>:<Port number> Example: 192.168.1.21:21000 To send to an IPv6 host, set [Host Name] using the following format: <IPv6 address>:<Port number> Example: [5aed:90a0:bc05:01d2:568a:2fc0:0001:12ee]:21000 |
UNIX/Linux
In some environments, detailed settings may be required in order to use FTP. For details, consult the
administrator for the network you are using.
administrator for the network you are using.
1.
Set a recipient address using the control panel.
Sample recipient settings:
Server side settings:
Host Name: | example |
Domain: | organization.company.com |
The user's home directory is /home/hsato, and /home/hsato/share is the data destination.
The machine's address settings:
<Protocol:>: | FTP |
[Host Name]: | example.organization.company.com |
[User Name]: | User name entered on the server |
[Password]: | Password for the above user |
Enter one of the following in [Folder Path]:
share (when using relative path)
/home/hsato/share (when using absolute path)
For a sample screen, see the example of Windows XP/Server 2003/Server 2008/Vista/7/Server 2008 R2/8/Server 2012 screen.
IMPORTANT |
To use the host name of the above example for [Host Name], it is necessary to use a DNS server. (This applies even if the machine and the FTP server are in the same subnet.) If no DNS server is available, the setting for [Host Name] should be specified using the IP address of the FTP server. Up to 128 alphanumeric characters can be entered for [Host Name] on the control panel. Also, up to 255 alphanumeric characters can be entered for [Folder Path]. Specify the server settings within the character limits. If you change the language of the touch panel display, [Host Name] and [Folder Path] may not appear correctly. If you want to send to an IPv4 host using an FTP port other than port 21, set [Host Name] using the following format: <IPv4 address of FTP server>:<Port number> Example: 192.168.1.21:21000 To send to an IPv6 host, set [Host Name] using the following format: <IPv6 address>:<Port number> Example: [5aed:90a0:bc05:01d2:568a:2fc0:0001:12ee]:21000 |