Connecting the Printer (LPD/RAW)
Configure the protocol settings.
If You Are Using Windows
When Installing the Printer Driver from the Beginning
1
Install the printer driver.
Following the procedure for automatically searching the printer on a network in "Printer Driver Installation Guide", install the printer driver.
 |
For details on the procedure for viewing "Printer Driver Installation Guide", see "Installation."
|
|
NOTE
|
When using LPDWhen the printer driver is installed using the above method, RAW is specified as the print application to be used. If you want to use LPD, install the printer driver using the above procedure, and then change a port.
|
When Changing a Port
1
Open the printer folder.
2
Right-click the icon for this printer, and then select [Printer properties] or [Properties] from the pop-up menu.
3
Perform the following procedure.
|
(1)
|
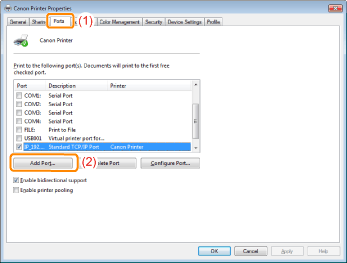
Display the [Ports] sheet.
|
|
(2)
|
Click [Add Port].
|
4
Select the port type.
|
(1)
|
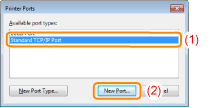
Select [Standard TCP/IP Port].
|
|
(2)
|
Click [New Port].
|
5
Click [Next].
6
Enter the IP address or name of the printer.
|
(1)
|
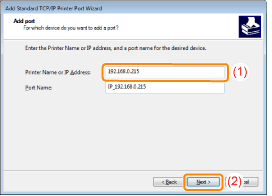
Enter the IP address or name* of the printer in [Printer Name or IP Address].
|
||
|
(2)
|
Click [Next].
|
|
IMPORTANT
|
||||
If the printer cannot be detectedThe following screen appears. Perform either of the following operations.
Follow the on-screen instructions and search again for the printer.
Specify the setting for [Device Type].
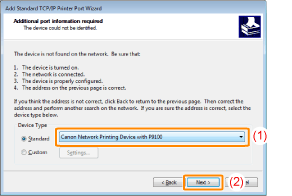 |
|
NOTE
|
If you are not sure about the value to enterThe value to be entered varies depending on how the IP address of the printer was set.
For more details, see "Values for Setting a Port" or ask your network administrator. |
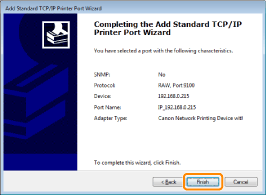
7
Click [Finish].
8
Click [Close].
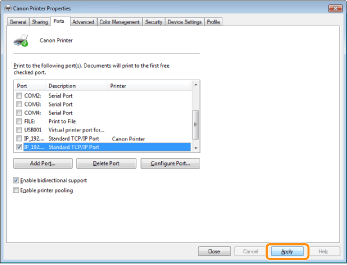
9
Click [Apply].
If you want to use LPD, proceed to Step 10.
If you want to use RAW, proceed to Step 11.
If you want to use LPD, change the port configuration information.
When using LPD printing, set up the LPR protocol using the procedure below.
|
(1)
|
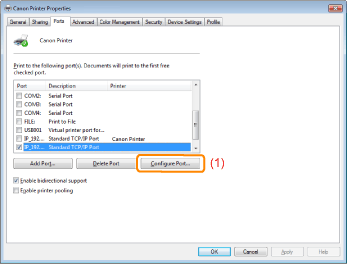
Click [Configure Port].
 |
|
(2)
|
Select [LPR].
|
|
(3)
|
Enter "lp" in [Queue Name].
|
|
(4)
|
Click [OK].
 |
Click [OK].
|
NOTE
|
When deleting an unnecessary portSelect the unnecessary port on the [Ports] sheet, and then click [Delete Port].
|
If You Are Using UNIX
This section describes the preparation for printing using LPD. For details on the procedure for printing using FTP, see "FTP Client."
|
IMPORTANT
|
About the setting procedureThe procedure described here is a setting example. Depending on the system environment, the setting procedure may be different.
Specify the settings also when using a computer on which UNIX OS is installed as a stand-alone workstation along the procedure described here.
|
1
Log in to the UNIX server as a root user.
|
IMPORTANT
|
If you do not have the root user permission on the UNIX serverConsult your network administrator.
|
2
Edit the "/etc/hosts" file to add the printer to the local network.
|
1.
|
Open the "/etc/hosts" file using a text editor.
|
||||||
|
2.
|
Add the following line.
|
||||||
|
3.
|
After saving the "/etc/hosts" file, exit the text editor.
|
|
IMPORTANT
|
Be sure to assign a fixed IP address to the printer.When printing from UNIX OS, be sure to assign a fixed IP address to the printer. For details on the procedure for setting the IP address, see "Setting the IP Address (IP v. 4)."
|
3
Set up the spooling system on the UNIX server.
Example of When Using Solaris 1.x
|
1.
|
Enter the following in the "/etc/printcap" file.
|
||||||
|
2.
|
Create the spool directory for the printer. Execute the following commands.
|
||||||
|
3.
|
Create the log file for the printer. Execute the following commands.
|
||||||
|
4.
|
Proceed to Step 4.
|
Example of When Using Solaris 2.x or Later
|
1.
|
Run "admintool."
|
||
|
2.
|
Select [Browse] → [Printers].
|
||
|
3.
|
Select [Edit] → [Add] → [Access to Printer].
|
||
|
4.
|
Enter an arbitrary print queue name in [Printer Name], and then enter the IP address or name of the printer in [Print Server].
|
||
|
5.
|
Select [OK].
|
||
|
6.
|
Proceed to Step 4.
|
Example of When Using HP-UX
|
1.
|
Run "SAM."
|
||
|
2.
|
Select [Printers and Plotters].
|
||
|
3.
|
Select [LP Spooler] from the [Printers and Plotters] menu.
|
||
|
4.
|
Select [Printers and Plotter] from the [LP Spooler] menu.
|
||
|
5.
|
Select [Add Remote Printer/Plotter] from the [Action] menu.
|
||
|
6.
|
Enter an arbitrary print queue name in [Printer Name], and then enter the IP address or name of the printer in [Remote System Name].
|
||
|
7.
|
Enter "lp" in [Remote Printer Name].
|
||
|
8.
|
Select [Remote Printer is on a BSD System].
|
||
|
9.
|
Select [OK].
|
||
|
10.
|
Proceed to Step 4.
|
Example of When Using IBM-AIX
|
1.
|
Run "SMIT."
|
||
|
2.
|
Select [Print Spooling] → [Add a Printer Queue] → [remote].
|
||
|
3.
|
Select [Standard processing].
|
||
|
4.
|
Enter an arbitrary print queue name in [remote queue name] and the IP address or name of the printer in [Hostname of Remote Server].
|
||
|
5.
|
Enter "lp" in [name of the queue] on the remote server.
|
||
|
6.
|
Enter "BSD" in [type of print spooler] on the remote server.
|
||
|
7.
|
Proceed to Step 4.
|
Enter the following commands and check if you can print.
|
Form:
|
lp -d <the print queue name> <the name of the file to be printed>
|
|
Input Example:
|
lp -d print_queue_name report
|