Authenticating Users and Managing Groups
Managing the users who use the machine and performing authentication of its use can prevent operation by third parties and unauthorized access.
User Authentication, an authentication application (login service), is the primary method for managing users. User Authentication authenticates users by using a user name and password registered for each user.
You can use user authentication to restrict usage of the machine and optimize settings for individual users.
User Authentication, an authentication application (login service), is the primary method for managing users. User Authentication authenticates users by using a user name and password registered for each user.
You can use user authentication to restrict usage of the machine and optimize settings for individual users.
To authenticate a user, first determine the authentication system, and then configure the necessary settings while considering the login method, role to be assigned to the user, and functions to be used.
IMPORTANT
To limit the authentication method to User Authentication (and not use System Manager ID for authentication) in the following situations, set [Prohibit Authentication Using Department ID and PIN] to [On]. [Prohibit Authentication Using Department ID and PIN]
When using the machine from a computer via a driver
When accessing the machine from the device management software
Authentication Systems
You can use the following two authentication systems:
Local Device (This Machine)
User information is managed in the database of the machine. This is called local device authentication.
User information can be registered for one user at a time, or user information can be saved to a file and imported to the machine to register multiple users at a time.
User information can be registered for one user at a time, or user information can be saved to a file and imported to the machine to register multiple users at a time.
You can register user information for up to 5,001 users.
When using local device authentication only, you can manage users in groups while also using Department ID Management.
When using local device authentication only, you can manage users in groups while also using Department ID Management.
External Authentication Server
The following types of servers can be used as an external authentication server:
Windows Server with Active Directory installed
Cloud server using Microsoft Entra ID
LDAP server
You can manage users using the user information registered to the server. This is called external server authentication.
* For details on the compatible Active Directory, LDAP servers, and Microsoft Entra ID, see the specifications of the authentication functions. Authentication Functions
Logging In to the Machine
Users registered to the local device can use either of the login methods below. Users registered to an external authentication server may only use keyboard authentication. The machine supports two-factor authentication for Picture Login and Remote UI login.
* Network login using the device management software does not support two-factor authentication.
Keyboard Authentication
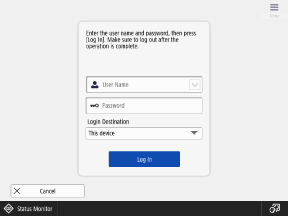
This login method can be used regardless of the authentication system.
Users log in with a user name and password using the keyboard displayed on the control panel. If the user name and password consist only of numbers, you can configure the settings to enable login using only the numeric keys.
Users log in with a user name and password using the keyboard displayed on the control panel. If the user name and password consist only of numbers, you can configure the settings to enable login using only the numeric keys.
Picture Login
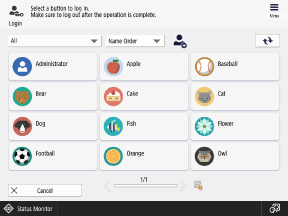
This login method can be used by users registered to the local device.
Users select their user name displayed on the control panel to log in, eliminating the need to enter a user name. You can also require users to enter a PIN or pattern to prevent unauthorized login.
Users select their user name displayed on the control panel to log in, eliminating the need to enter a user name. You can also require users to enter a PIN or pattern to prevent unauthorized login.
* Up to 200 users can be displayed on the control panel.
NOTE
Logging in To Remote UI
You can use a web browser on a computer to log in to Remote UI.
Roles
User authentication can be used to configure privileges (roles) for each user to control the operations they can perform.
Configurable Roles
By assigning roles to users according to their responsibilities, the various management tasks of the machine can be shared.
GeneralUser | This is a general user. |
DeviceAdmin | In addition to the operations of a general user, a DeviceAdmin can configure the print, scan, fax, copy, and other basic settings and change the device information settings. |
NetworkAdmin | In addition to the operations of a general user, a NetworkAdmin can change the network settings. |
Administrator | An Administrator can perform all operations of the machine. |
* For details about the settings that can be changed by a DeviceAdmin and NetworkAdmin, see the following:
Using the Attributes of Active Directory/LDAP Server/Microsoft Entra ID
When external server authentication is used, you can determine the roles according to the server attributes. You can use the character string registered to the attributes as the role name, and you can also set conditions and assign specific roles when those conditions are met.
Using ACCESS MANAGEMENT SYSTEM to Specify Roles
In environments where ACCESS MANAGEMENT SYSTEM can be used, you can assign functions available to each role and create new roles.
Functions Available with User Authentication
You can use the following functions and settings during user authentication to allow users to efficiently operate the machine.
Optimizing User Settings (Personalization)
By default, the personalization function is enabled when using user authentication. This function saves the various settings of the machine customized by the user and applies them each time that user logs in. This enables efficient operation of the machine without the user having to change the same settings or operations each time. Using the Personalization Function
Managing Users as a Group (Department ID Management)
Use Department ID Management to collectively manage users registered to the local device in a group (Department ID) such as a company department.
By using Department ID Management, you can monitor usage of the machine and restrict the number of pages that can be printed for each Department ID, and you can require users to enter a PIN to perform certain operations. This is useful for adjusting operations of the machine and for improving cost awareness and security.
You can also register a common user for each Department ID and allow operations in which multiple users can use that common user.
To use Department ID Management, you must configure the system manager information settings, register and specify the Department ID, and then enable Department ID Management.
By using Department ID Management, you can monitor usage of the machine and restrict the number of pages that can be printed for each Department ID, and you can require users to enter a PIN to perform certain operations. This is useful for adjusting operations of the machine and for improving cost awareness and security.
You can also register a common user for each Department ID and allow operations in which multiple users can use that common user.
To use Department ID Management, you must configure the system manager information settings, register and specify the Department ID, and then enable Department ID Management.
* To share an address list among multiple users, use a user group instead of Department ID Management. Sharing Destinations in a Group (User Group)
Using Personal Folders
Personal Folder is a personal folder that can be used by a login user. Shared folders and folders on the file server can be specified as Personal Folders.
The Personal Folder specification method is selected in advance by the administrator. Each user uses their Personal Folder according to this specification method.
The Personal Folder specification method is selected in advance by the administrator. Each user uses their Personal Folder according to this specification method.